Import Avro data
If you want to import your data in Memgraph using Apache Avro serialization, you need to know the Avro schema of your data. This is necessary for deserializing the data. Each schema contains a single schema definition, so there should be a separate schema for each data representation you want to import into Memgraph.
Datatype mapping
Avro data types will be flexibly mapped to the target schema, that is, Avro and openCypher types do not need to match exactly. Use the table below for data type mappings:
| Avro Data Type | Cypher Casting Function |
|---|---|
| bool | toBoolean |
| float | toFloat |
| int | toInteger |
Example
Let's assume we have the following schemas coming out of their respective topics
avroStreamProfile, avroStreamCompany, avroStreamWorksAt:
profile_schema = """ {
"namespace": "example.avro",
"name": "Person",
"type": "record",
"fields": [
{"name": "name", "type": "string"},
{"name": "age", "type": "int"},
{"name": "email", "type": "string"},
{"name": "address", "type": "string"}
]
}"""
company_schema = """{
"namespace": "example.avro",
"name": "Company",
"type": "record",
"fields": [
{"name": "name", "type": "string"},
{"name": "address", "type": "string"}
]
} """
works_at_schema = """ {
"namespace": "example.avro",
"name": "Works_At",
"type": "record",
"fields": [
{"name": "name", "type": "string"},
{"name": "company", "type": "string"}
]
}
"""
We can use the schemas to build the following graph:
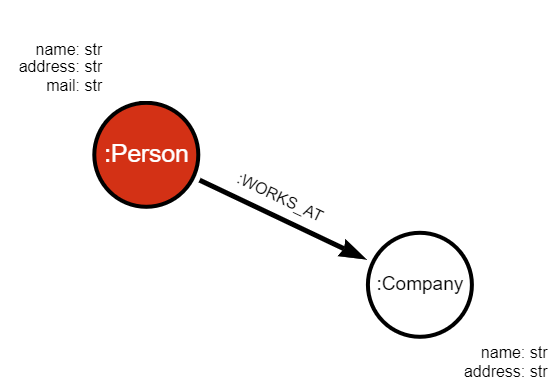
Deserialization
Data received by the Memgraph consumer is a byte array and needs to be deserialized. The following method will help you deserialize your data with the help of Confluent Kafka:
from confluent_kafka.schema_registry import SchemaRegistryClient
from confluent_kafka.schema_registry.avro import AvroDeserializer
def process_record_confluent(record: bytes, src: SchemaRegistryClient, schema: str):
deserializer = AvroDeserializer(schema_str=schema, schema_registry_client=src)
return deserializer(record, None) # returns dict
Transformation modules
Before consuming data from a stream, we need to implement transformation modules that will produce queries. In order to create a transformation module, you need to:
- Create a Python module
- Save it into the Memgraph's query-modules directory (default:
/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules) - Load it into Memgraph either on startup (automatically) or by running the
CALL mg.load_allquery
Example for the profile_transformation module:
@mgp.transformation
def profile_transformation(messages: mgp.Messages) -> mgp.Record(query = str, parameters=mgp.Nullable[mgp.Map]):
result_queries = []
for i in range(messages.total_messages()):
message_avro = messages.message_at(i)
msg_value = message_avro.payload()
message = process_record_confluent(msg_value, src= SchemaRegistryClient({'url': 'http://localhost:8081'}), schema=profile_schema)
result_queries.append(mgp.Record (
query=f'CREATE (p: Person {{ name: "{message["name"]}", age: ToInteger({message["age"]}), address: "{message["address"]}", email:"{message["email"]}" }});' ,
parameters=None
))
return result_queries
Creating streams
To import data into Memgraph, we need to create a stream for each topic and apply our transformation module on incoming data:
CREATE KAFKA STREAM avroStreamProfile TOPICS avro-stream-profile TRANSFORM avro_transform.profile_transformation;
CREATE KAFKA STREAM avroStreamCompany TOPICS avro-stream-company TRANSFORM avro_transform.company_transformation;
CREATE KAFKA STREAM avroStreamWorksAt TOPICS avro-stream-worksat TRANSFORM avro_transform.works_at_transformation;
To start the streams, execute the following query:
START ALL STREAMS;
Run the following query to check if all the streams were started correctly:
SHOW STREAMS;
You can also check the node counter in Memgraph Lab (Overview tab) to see if new nodes and relationships are arriving.
Next steps
Check out the example-streaming-app on GitHub to see how Memgraph can be connected to a Kafka stream.