Importing data from Kafka streams
Memgraph can natively ingest streaming data from upstream sources using Apache Kafka and Confluent Platform. To import data using streams, you must:
- Start Memgraph and connect to it
- Define a transformation module
- Create the stream in Memgraph
- Start ingesting data from the stream
Prerequisites
In order to create a Kafka pipeline, you must have:
- a working Kafka stream
- access to a running Memgraph instance.
Importing data
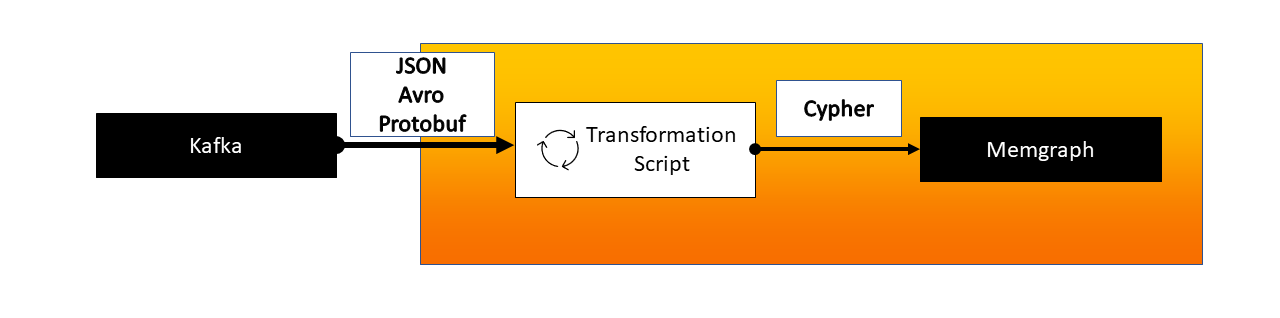
When importing data, we should be aware of all the different nodes and relationships our stream contains. The best practice is to have a dedicated topic for each message type in order to parse the data more efficiently. Each topic requires a separate procedure within a single transformation module to handle the conversion. Once we create a stream in Memgraph and start ingesting data, we are all set to analyze it.
1. Start Memgraph
Start Memgraph and establish a connection to the database.
If you are starting Memgraph using a Docker image and would like to access configuration files or logs, be sure to run the image with the following volumes:
-v mg_log:/var/log/memgraph-v mg_etc:/etc/memgraph
2. Define the transformation module
A transformation module is a user-defined program that receives data from Kafka and returns processed data in the form of Cypher queries. The most common formats received from Kafka are:
Transformation modules can be written in either Python or C. Take a look at the Python API guide for an example of how to implement transformation modules in Python.
When started, Memgraph will automatically attempt to load the query modules from
all *.so and *.py files it finds in the default
/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules directory. You can point to a different
directory by changing or extending the --query-modules-directory flag in the
main configuration file (/etc/memgraph/memgraph.conf) or define it within a
command-line parameter when using Docker.
Please remember that if you are using Memgraph Platform image, you should pass
configuration flags within MEMGRAPH environmental variable (e.g. docker run -e MEMGRAPH="--bolt-port=7687" memgraph/memgraph-platform) and if you are using
any other image, you should pass them as arguments after the image name (e.g.,
memgraph/memgraph-mage --bolt-port=7687 --query-modules-directory=path/path).
Transfer a transformation module into a Docker container
1. Open a new terminal and find the CONTAINER ID of the Memgraph Docker
container:
docker ps
2. Copy a file from your current directory to the container with the command:
docker cp ./trans_module.py <CONTAINER ID>:/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules/trans_module.py
The file is now inside your Docker container.
If the transformation module has been added to the directory while the Memgraph instance was already running, you need to load it manually by using the following query:
CALL mg.load('<transformation_name>');
or
CALL mg.load_all;
If you want to check if your module has properly loaded in Memgraph run:
CALL mg.transformations() YIELD *;
You should see an output similar to the following:
+-------------------------------------------------------+
| name |
+-------------------------------------------------------+
| "transformation_name.my_transformation_module" |
+-------------------------------------------------------+
3. Create a stream in Memgraph
First, make sure Kafka and Memgraph are running, and there is a topic available. Then, make sure the transformation module is loaded
Create the stream in Memgraph with the following query:
CREATE KAFKA STREAM <stream_name>
TOPICS <topic1>[, <topic2>, ...]
TRANSFORM <transformation_module.transformation_procedure>
[BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS <bootstrap servers>];
You need to create one stream for each topic and procedure you have.
For more options and information about the CREATE .. STREAM query check out
the reference guide.
4. Start ingesting data from the stream
The previous query only created the streams. To start streaming data, execute the following query:
START STREAM <stream_name>;
or
START ALL STREAMS;
Your data should be slowly arriving in your Memgraph instance. To check if everything is working, run the following query:
CHECK STREAM <stream_name>;
or
SHOW STREAMS;
You can also check the node counter in Memgraph Lab (Overview tab) to see if new nodes and relationships are arriving.
For all the other stream commands, check out the reference guide.
Logs
Errors and notifications regarding streams are contained in Memgraph's log files
which can be found at /var/log/memgraph/memgraph_<date>.log Look for the name
of your stream in the log file to find the error. You can use the grep command
to search for the stream in the log file:
grep '<stream_name>' /var/log/memgraph/memgraph_<date>.log
What next?
Take a look at the tutorial we made to help you connect Memgraph and Kafka. Learn more about the query power of Cypher language, or check out MAGE - an open-source repository that contains graph algorithms and modules that can help you tackle the most interesting and challenging graph analytics problems. If you are using Memgraph Lab, a visual user interface for running queries and visualizing graph data, you might be interested in the Graph Style Script language that will help you bedazzle your graphs. Above all, enjoy your graph database!


