Importing data from Kafka streams
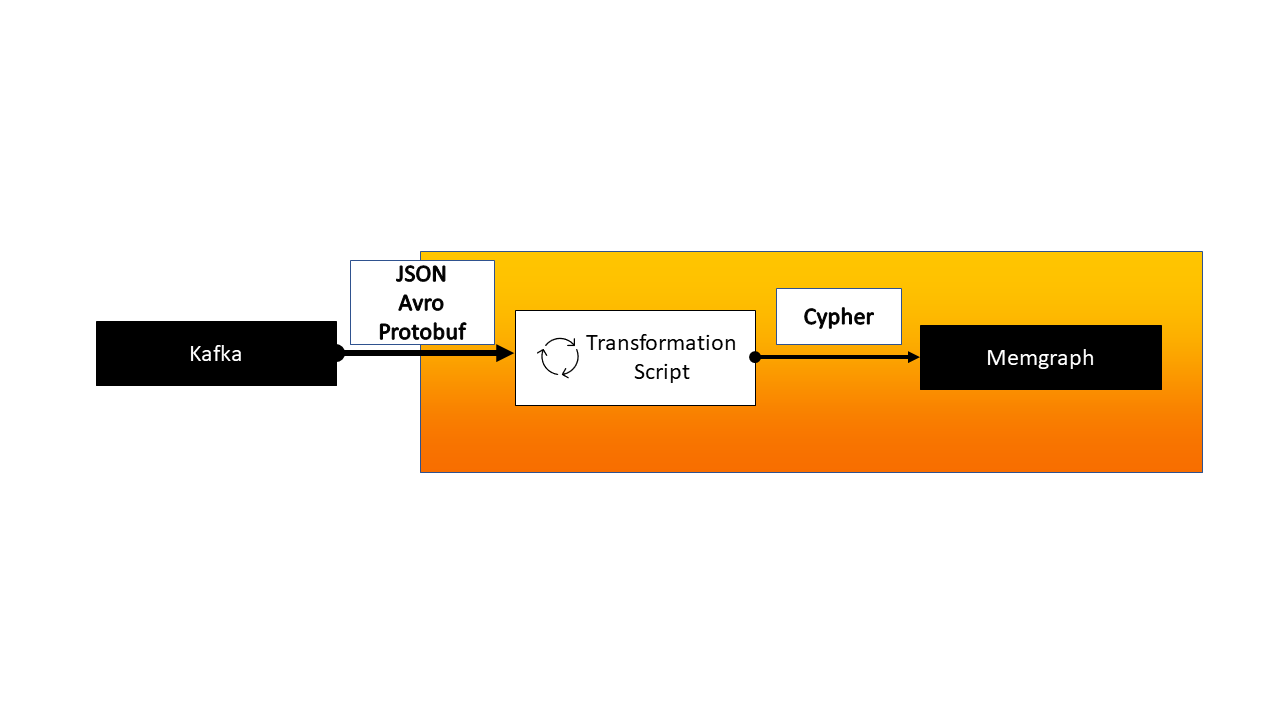
Memgraph can natively ingest streaming data from upstream sources using Apache Kafka and Confulent Platform. To import data using streams, a user must:
- Start Memgraph with Kafka cofiguration
- Define a transformation module
- Create the stream in Memgraph
- Start ingesting data from the stream
Prerequisites
To create a Kafka pipeline, you must meet the following prerequisites:
- Have a working Kafka stream
- Have access to a Memgraph instance
All of the errors regarding streams are contained in Memgraph's
log files which can be found at /var/log/memgraph/memgraph_<date>.log Just
search for the name of your stream in the log file to find the error. You can
use the grep command to search for the stream in the log file:
grep '<stream_name>' /var/log/memgraph/memgraph_<date>.log
Importing data
When importing data, we have to take note of all the different nodes and relationships our stream contains. The best practice is to handle them all separately. Each node and each relationship type should have a dedicated topic. This kind of strategy always assumes one message represents one node or one relationship.
Topics that contain multiple differently formatted messages should be avoided whenever possible. Sending data in different topics allows for better control of when either data type is created. It is easier to parse the data from a single topic for events of the same type. You only need to create a separate transformation module to handle the conversion.
1. Start Memgraph with Kafka configuration
As Memgraph can only connect to one Kafka cluster at once, the list of bootstrap
servers can be explicitly set by the --kafka-bootstrap-servers configuration
option. This can be edited in the memgraph.conf file or supplied as a
command-line parameter (e.g., when using Docker).
2. Define the transformation module
A transformation module is a user-defined program that receives data from Kafka and returns processed data in the form of Cypher queries. The most common formats received from Kafka are JSON, Avro, or Protobuf. Transformation modules can be written in either Python or C.
By default, all of the modules load on startup. If you want to change the
directory in which Memgraph searches for transformation modules, just change or
extend the --query-modules-directory flag in the main configuration file
(/etc/memgraph/memgraph.conf) or supply it as a command-line parameter (e.g.,
when using Docker).
Take a look at Python API guide for an example of how to implement transformation modules in Python.
Load the transformation module from /usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules by using
the following query:
CALL mg.load('<transformation_name>');
If you want to check if your module has properly loaded in Memgraph, you can check it with:
CALL mg.transformations() YIELD *;
You should see an output similar to the following:
+-------------------------------------------------------+
| name |
+-------------------------------------------------------+
| "transformation_name.my_transformation_module" |
+-------------------------------------------------------+
3. Create a stream in Memgraph
Creating, starting, and deleting the streams can be done with Cypher queries. Check out the list of available stream commands.
To import data, first, make sure Kafka and Memgraph are running and there is a topic available.
After making sure the transformation module is loaded, connect Memgraph to the stream with the following query:
CREATE KAFKA STREAM <name_of_the_stream>
TOPICS <name_of_the_topics_created>
TRANSFORM <transformation_module_name.transformation>;
4. Start ingesting data from the stream
This query only created the stream. To start streaming data, execute the following query:
START STREAM <name_of_the_stream>
Your data should be slowly arriving in your Memgraph instance. To check if everything is working, run the following query:
CHECK STREAM <stream_name>