Importing Cypher queries (CYPHERL format)
If your data is in the form of Cypher queries (for example, CREATE and MERGE
clauses) within a CYPHERL file it can be imported via Memgraph Lab or
mgconsole.
The benefit of importing data using the CYPHERL file is that you need only one file to import both nodes and relationships. But it can be tricky to actually write the queries for creating nodes and relationships yourself. If you haven't written any queries yet, check our Cypher manual.
Importing via Memgraph Lab
Once you Memgraph instance in running and you've connected to it via Memgraph Lab, go to the Import & Export section. To Import Data select the CYPHERL file or drag and drop it into Memgraph Lab.
Importing via mgconsole
Once Memgraph is running, Cypher queries are imported by running mgconsole in a non-interactive mode and importing data saved in a CYPHERL file.
You can import queries saved in e.g. queries.cypherl by issuing the following
shell command:
mgconsole < queries.cypherl
If you installed and started Memgraph using Docker, you will need to run the client using the following command:
docker run -i --entrypoint=mgconsole memgraph/memgraph-platform --host HOST < queries.cypherl
Remember to replace HOST with valid IP of the
container
and to define the correct Memgraph Docker image you are using as well as the
correct path to the file.
Below, you can find two examples of how to import data within the .cypherl file
based on the complexity of your data:
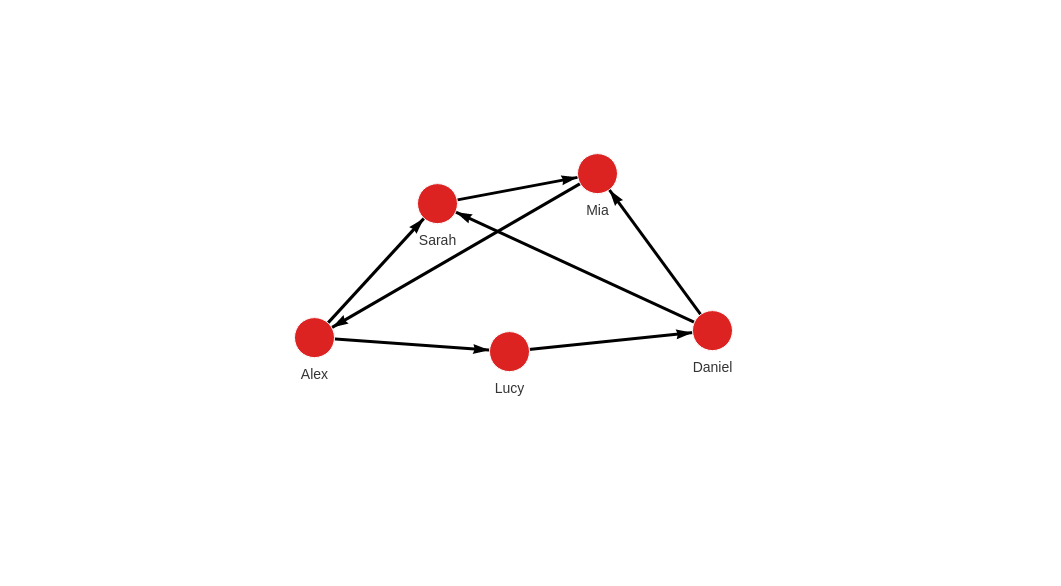
One type of nodes and relationships
Let's import data from queries.cypherl file with the following content:
CREATE (:Person {id: "100", name: "Daniel", age: 30, city: "London"});
CREATE (:Person {id: "101", name: "Alex", age: 15, city: "Paris"});
CREATE (:Person {id: "102", name: "Sarah", age: 101, city: "London"});
CREATE (:Person {id: "103", name: "Mia", age: 25, city: "Zagreb"});
CREATE (:Person {id: "104", name: "Lucy", age: 21, city: "Paris"});
MATCH (u:Person), (v:Person) WHERE u.id = "100" AND v.id = "102" CREATE (u)-[:IS_FRIENDS_WITH]->(v);
MATCH (u:Person), (v:Person) WHERE u.id = "100" AND v.id = "103" CREATE (u)-[:IS_FRIENDS_WITH]->(v);
MATCH (u:Person), (v:Person) WHERE u.id = "101" AND v.id = "104" CREATE (u)-[:IS_FRIENDS_WITH]->(v);
MATCH (u:Person), (v:Person) WHERE u.id = "101" AND v.id = "102" CREATE (u)-[:IS_FRIENDS_WITH]->(v);
MATCH (u:Person), (v:Person) WHERE u.id = "102" AND v.id = "103" CREATE (u)-[:IS_FRIENDS_WITH]->(v);
MATCH (u:Person), (v:Person) WHERE u.id = "103" AND v.id = "101" CREATE (u)-[:IS_FRIENDS_WITH]->(v);
MATCH (u:Person), (v:Person) WHERE u.id = "104" AND v.id = "100" CREATE (u)-[:IS_FRIENDS_WITH]->(v);
The first five queries create nodes for people, and the rest of the queries create relationships between these nodes.
- Docker 🐳
- Linux
If you installed Memgraph using Docker, run the client using the following command, but be careful of four things:
- Use the first command in Docker installed on Linux and macOS, but use the second command in Windows because PowerShell doesn't support the < character.
- Check the image name you are using is correct:
- If you downloaded Memgraph Platform, leave the current image name
memgraph/memgraph-platform. - If you downloaded MemgraphDB, replace the current image name with
memgraph/memgraph. - If you downloaded MAGE, replace the current image name with
memgraph/memgraph-mage. - Remember to replace
HOSTwith a valid IP of the container (see the guide on working with Docker). - Check that the paths of the files you want to import are correct.
Linux and macOS
docker run -i --entrypoint=mgconsole memgraph/memgraph-platform --host HOST < queries.cypherl
Windows PowerShell:
cmd.exe /c "docker run -i --entrypoint=mgconsole memgraph/memgraph-platform --host HOST < queries.cypherl"
For more information about mgconsole options run:
docker run -i --entrypoint=mgconsole memgraph/memgraph-platform --help
mgconsole < queries.cypherl
For more information about mgconsole options run:
mgconsole --help
This is how the graph should look like in Memgraph after the import:
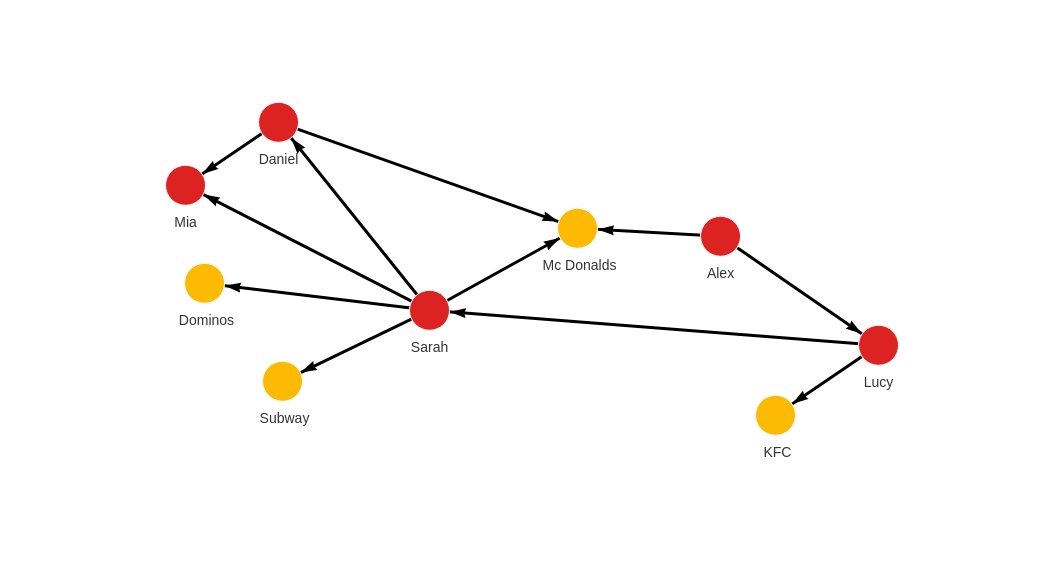
Multiple types of nodes and relationships
Let's import data from queries.cypherl file with the following content:
CREATE (p:Person {id: "100", name: "Daniel", age: 30, city: "London"});
CREATE (p:Person {id: "101", name: "Alex", age: 15, city: "Paris"});
CREATE (p:Person {id: "102", name: "Sarah", age: 17, city: "London"});
CREATE (p:Person {id: "103", name: "Mia", age: 25, city: "Zagreb"});
CREATE (p:Person {id: "104", name: "Lucy", age: 21, city: "Paris"});
CREATE (r:Restaurant {id: "200", name: "McDonalds", menu: "Fries BigMac McChicken Apple Pie"});
CREATE (r:Restaurant {id: "201", name: "KFC", menu: "Fried Chicken Fries Chicken Bucket"});
CREATE (r:Restaurant {id: "202", name: "Subway", menu: "Ham Sandwich Turkey Sandwich Foot-long"});
CREATE (r:Restaurant {id: "203", name: "Dominos", menu: "Pepperoni Pizza Double Dish Pizza Cheese filled Crust"});
MATCH (u:Person), (v:Person) WHERE u.id = "100" AND v.id = "103" CREATE (u)-[:IS_FRIENDS_WITH {met_in: "2014"}]->(v);
MATCH (u:Person), (v:Person) WHERE u.id = "101" AND v.id = "104" CREATE (u)-[:IS_FRIENDS_WITH {met_in: "2001"}]->(v);
MATCH (u:Person), (v:Person) WHERE u.id = "102" AND v.id = "100" CREATE (u)-[:IS_FRIENDS_WITH {met_in: "2005"}]->(v);
MATCH (u:Person), (v:Person) WHERE u.id = "102" AND v.id = "103" CREATE (u)-[:IS_FRIENDS_WITH {met_in: "2017"}]->(v);
MATCH (u:Person), (v:Person) WHERE u.id = "103" AND v.id = "104" CREATE (u)-[:IS_FRIENDS_WITH {met_in: "2005"}]->(v);
MATCH (u:Person), (v:Person) WHERE u.id = "104" AND v.id = "102" CREATE (u)-[:IS_FRIENDS_WITH {met_in: "2021"}]->(v);
MATCH (u:Person), (v:Restaurant) WHERE u.id = "100" AND v.id = "200" CREATE (u)-[:ATE_AT {liked: true}]->(v);
MATCH (u:Person), (v:Restaurant) WHERE u.id = "102" AND v.id = "202" CREATE (u)-[:ATE_AT {liked: false}]->(v);
MATCH (u:Person), (v:Restaurant) WHERE u.id = "102" AND v.id = "203" CREATE (u)-[:ATE_AT {liked: false}]->(v);
MATCH (u:Person), (v:Restaurant) WHERE u.id = "102" AND v.id = "200" CREATE (u)-[:ATE_AT {liked: true}]->(v);
MATCH (u:Person), (v:Restaurant) WHERE u.id = "103" AND v.id = "201" CREATE (u)-[:ATE_AT {liked: true}]->(v);
MATCH (u:Person), (v:Restaurant) WHERE u.id = "104" AND v.id = "201" CREATE (u)-[:ATE_AT {liked: false}]->(v);
MATCH (u:Person), (v:Restaurant) WHERE u.id = "101" AND v.id = "200" CREATE (u)-[:ATE_AT {liked: true}]->(v);
The first five queries create nodes for people, and the following four queries create nodes for restaurants. The rest of the queries are used to define relationships between nodes. As said before, you can define different types of nodes and relationships in one file.
- Docker 🐳
- Linux
If you installed Memgraph using Docker, run the client using the following command, but be careful of four things:
- Use the first command in Docker installed on Linux and macOS, but use the second command in Windows because PowerShell doesn't support the < character.
- Check the image name you are using is correct:
- If you downloaded Memgraph Platform, leave the current image name
memgraph/memgraph-platform. - If you downloaded MemgraphDB, replace the current image name with
memgraph/memgraph. - If you downloaded MAGE, replace the current image name with
memgraph/memgraph-mage. - Remember to replace
HOSTwith a valid IP of the container (see the guide on working with Docker). - Check that the paths of the files you want to import are correct.
Linux and macOS
docker run -i --entrypoint=mgconsole memgraph/memgraph-platform --host HOST < queries.cypherl
Windows Powershell
cmd.exe /c "docker run -i --entrypoint=mgconsole memgraph/memgraph-platform --host HOST < queries.cypherl"
For more information about mgconsole options run:
docker run -i --entrypoint=mgconsole memgraph/memgraph-platform --help
mgconsole < queries.cypherl
For more information about mgconsole options run:
mgconsole --help
This is how the graph should look like in Memgraph after the import: