How to use query modules
Query modules are extensions of the Cypher query language. They are groups of
procedures and functions written in C, C++, Python, and Rust and
bundled up in either *.so or *.py query modules files.
Some query modules are built-in, and others, like those that can help you solve complex graph issues, are available as part of the MAGE library you can add to your Memgraph installation. The library is already included if you are using Memgraph Platform or Memgraph MAGE Docker images to run Memgraph.
You can also implement custom query modules.
Regardless of where they come from and who wrote them, all modules need to be loaded into Memgraph so that they can be called while querying the database. They are either loaded automatically when Memgraph starts or manually if they were added while Memgraph was already running.
On this page, you will find the answers to the following questions regarding query modules:
- How to import the MAGE library and its query modules into Memgraph?
- How to implement custom query modules?
- How to install external Python packages?
- How to list all loaded .py query modules?
- How to list all loaded procedures and their signatures?
- How to load a query module?
- How to call a query module procedure?
- How to control the memory usage of a procedure?
- How to change the default query module directories?
How to import the MAGE library and its query modules into Memgraph?
Memgraph Advanced Graph Extensions, MAGE to friends, is an open-source repository that contains graph algorithms and procedures as query modules, thus giving everyone the tools they need to tackle the most interesting and challenging graph analytics problems.
If you installed Memgraph with Docker using the memgraph-platform or
memgraph-mage images, the MAGE library is already loaded into Memgraph, and
you can proceed to call any of the available
procedures.
Otherwise, please check the MAGE installation guide.
How to implement custom query modules?
If you need to expand the Cypher language with custom procedures, Memgraph provides public APIs for writing custom query modules in Python, C/C++ and Rust.
Please check the reference guide on implementing custom query modules that will provide you with the C and Python APIs and give an example to help you start implementing a custom query module.
You can develop query modules in Python directly from Memgraph Lab (v2.0 or newer). To start, just navigate to Query Modules and click on New Module.
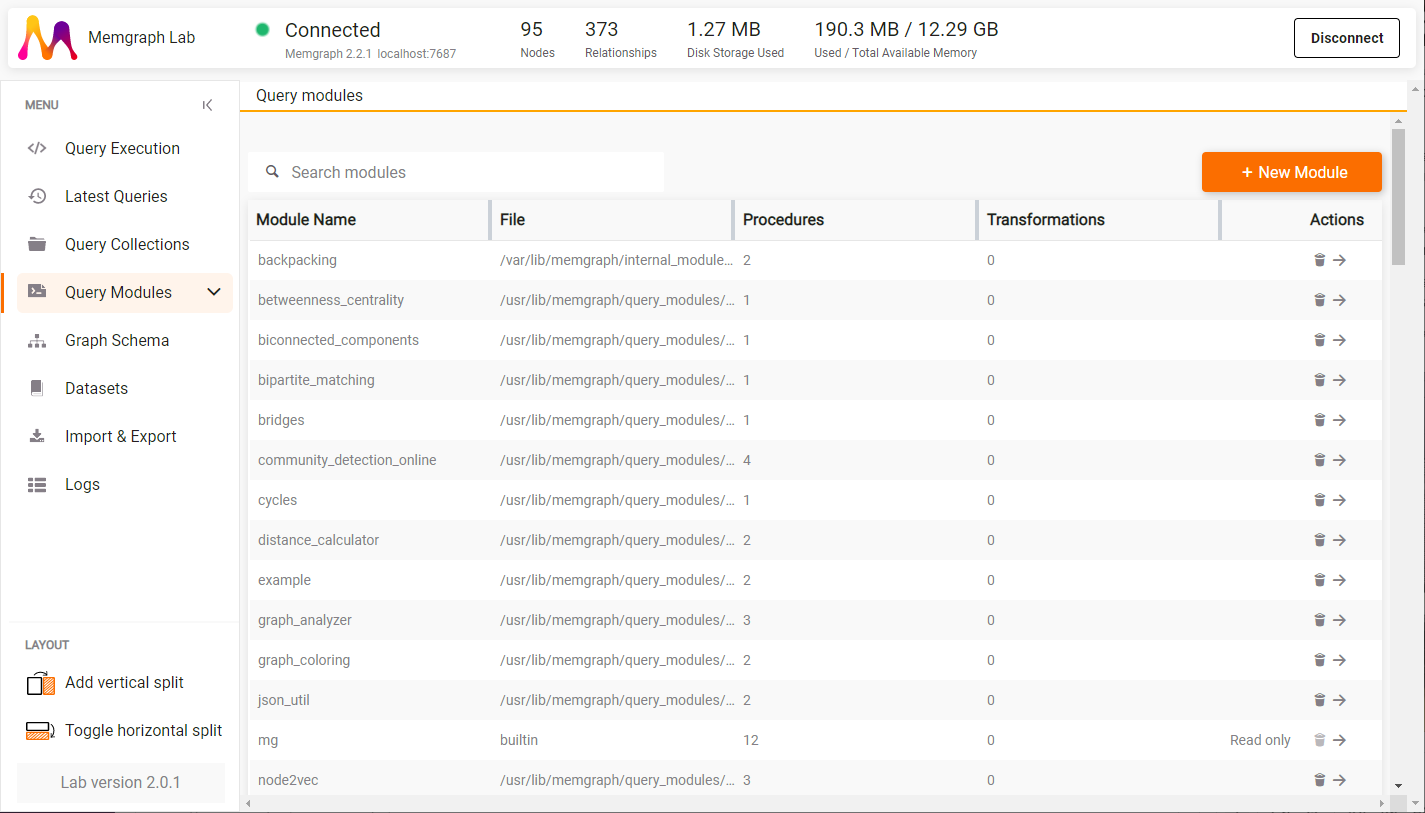
If you want to use an external Python library, read instructions on how to install it.
How to install external Python libraries?
It is possible to install Python libraries that are not already included with
Memgraph installation. For example, to install pandas with Memgraph running
inside a Docker container, run the following command in the terminal:
docker exec -i -u root <container_id> bash -c "apt install -y python3-pip &&
pip install pandas"
Don't forget to replace <container_id> with the appropriate value,
which you can find by running docker ps command in the terminal.
If you are starting Memgraph with Docker Compose, write the following commands in the Dockerfile:
FROM memgraph/memgraph:latest
USER root
RUN apt install -y python3-pip
RUN pip install pandas
USER memgraph
It is important that you install Python library as a root user, rather than the default memgraph user.
How to list all loaded .py query modules?
To list the value of an is_editable flag and the absolute path of each Python
query module file in all the query module directories, run the following query:
CALL mg.get_module_files() YIELD *;
Check the reference guide for more utility procedures for query modules.
How to list all loaded procedures, user-defined functions and their signatures?
To list loaded procedures and their signatures, run the following query:
CALL mg.procedures() YIELD *;
On the other side, if you are interested in listing all user-defined functions, run this query:
CALL mg.functions() YIELD *;
Check the reference guide for more utility procedures for query modules.
How to load a query module?
Upon startup, Memgraph will attempt to load the query modules from all *.so
and *.py files it finds in the default query module directories
(/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules and /var/lib/memgraph/internal_modules).
You can also (re)load all or specific modules manually.
To (re)load all query modules in all the query module directories, run the following query:
CALL mg.load_all();
If the response is an Empty set (x.x sec) and there are no error messages, the
update was successful.
To (re)load a specific module, run the following query:
CALL mg.load("py_example");
If the response is an Empty set (x.x sec) and there are no error messages, the
update was successful.
For more information on loading procedures please read the reference guide.
How to call a query module procedure?
Each query module file corresponds to one query module, and file names are
mapped as query module names. For example, example.so will be mapped as
example module, and py_example.py will be mapped as py_example module. If
each module file has a procedure called procedure defined, those procedures
would be mapped in the Cypher query language as example.procedure() and
py_example.procedure(), respectively.
The syntax for calling procedures in loaded query modules is:
CALL module.procedure(arg1, arg2, ...) YIELD res1, res2, ...;
Each procedure returns zero or more records, where each record contains named
fields. The YIELD part is used to select fields we are interested in. If the
procedure doesn't return any fields, the YIELD part can be omitted.
Procedures can also be a part of a larger query:
MATCH (node) CALL module.procedure(node) YIELD result RETURN *;
For more information and constrictions on calling procedures, please read the reference guide.
How to call a user-defined function?
Similarly, query procedure rules apply to the functions. Although their context
is different, the mechanism behind functions maps the written functions to
example.function() and py_example.function() respectively, just as was the
case above.
The syntax for calling functions in loaded query modules is similar to the built-in functions, with the difference being case sensitivity. User-defined functions do have a case sensitive name, while builtin ones don't:
RETURN example.function();
Since functions do not require a heavy context around them, they are easily nested and combined with other Cypher syntax.
MATCH (node) CALL module.procedure(module.function(node)) YIELD result RETURN ABS(result);
How to control the memory usage of a procedure?
When a procedure cannot yield results using the default 100 MB, you can increase the maximum memory usage by adding the following clause in the query:
CALL module.procedure(arg1, arg2, ...) PROCEDURE MEMORY LIMIT 100 KB YIELD res1, res2, ...;
CALL module.procedure(arg1, arg2, ...) PROCEDURE MEMORY LIMIT 100 MB YIELD res1, res2, ...;
CALL module.procedure(arg1, arg2, ...) PROCEDURE MEMORY UNLIMITED YIELD res1, res2, ...;
The limit can be specified to a specific value (in KB or MB) or set to
UNLIMITED.
For more information on controlling the memory usage of procedures please read the reference guide.
How to change the default query module directories?
If you want to change the default query module directories
(/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules and /var/lib/memgraph/internal_modules),
that is, the directories in which Memgraph searches for query modules, change
the --query-modules-directory flag in the main configuration file
(/etc/memgraph/memgraph.conf) or supply it as a command-line parameter (e.g.
when using Docker).
You can find all the configuration settings in the reference guide or check our guide on how to change the Memgraph configuration.
