Connect to data streams using Cypher queries
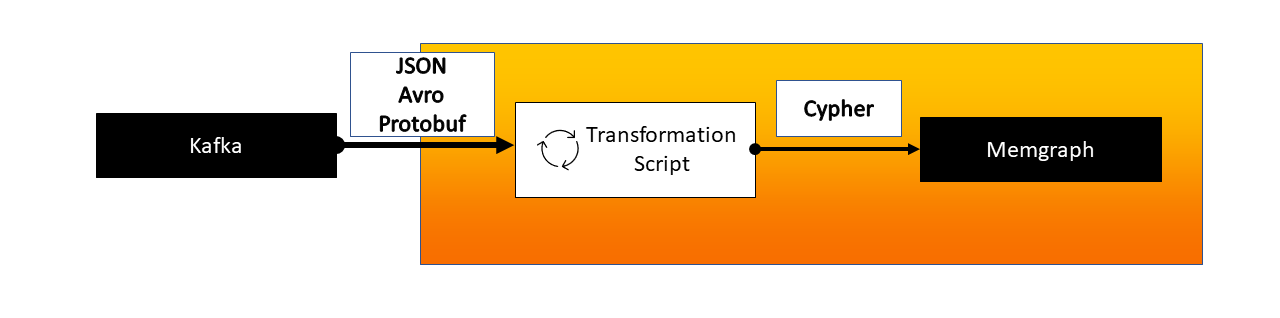
Memgraph can natively ingest streaming data from upstream sources using Apache Kafka, Redpanda and Pulsar.
The following page instructs how to connect to data streams to ingest the data and manage the connection using Cypher queries. The connection to streams can also be managed through the Stream section in the Memgraph Lab.
To import data from streams using Cypher queries:
- Start Memgraph and connect to the database
- Create and load a transformation module into Memgraph
- Create a stream in Memgraph
- Start ingesting data from the stream
If you need a Kafka stream to play around with, we've provided some at Awesome Data Stream!
Create and load a transformation module into Memgraph
A transformation module is a set of user-defined transformation procedures written in C or Python that act on data received from a streaming engine. Transformation procedures instruct Memgraph on how to transform the incoming messages to consume them correctly.
Once you created a Python or a shared library file
(module),
save the file into the Memgraph's query_modules or internal_modules
directory (default: /usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules and
/var/lib/memgraph/internal_modules/). If you are using Docker, you need to transfer
the transformation module file into the Docker
container.
If you are using Memgraph Lab you can create transformation module in Python within the application.
The best practice is to have a dedicated topic for each message type to parse the data more efficiently. Each topic requires a separate procedure within a single transformation module to handle the conversion.
Load the transformation module
When started, Memgraph will automatically attempt to load the transformation
modules from all *.so and *.py files it finds in the default
/usr/lib/memgraph/query_modules and /var/lib/memgraph/internal_modules directories.
You can point to a different directory by changing or extending the
--query-modules-directory flag in the main configuration file
(/etc/memgraph/memgraph.conf). If you need help changing the configuration
file, check out the how-to guide. You can also
define the flag within a command-line parameter when using Docker.
Please remember that if you are using Memgraph Platform image, you should pass
configuration flags within MEMGRAPH environment variable (e.g. docker run -p
7687:7687 -p 3000:3000 -p 7444:7444 -e MEMGRAPH="--log-level=TRACE"
memgraph/memgraph-platform) and if you are using any other image, you should
pass them as arguments after the image name (e.g., ... memgraph/memgraph-mage
--log-level=TRACE --query-modules-directory=path/path).
If the transformation module has been added to the directory while the Memgraph instance was already running, you need to load it manually by using the following query:
CALL mg.load('transformation_name');
or
CALL mg.load_all();
Check the transformation module
If you want to check if your module has properly loaded in Memgraph run:
CALL mg.transformations() YIELD *;
You should see an output similar to the following:
+------------------+------------------------------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+
| is_editable | name | path |
+------------------+------------------------------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------|
| `true` | "transformation_module.procedure" | `/var/lib/memgraph/internal_modules/transformation_module.py |
+------------------+------------------------------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+
Create a stream in Memgraph
To create a stream with a Cypher query, you first need to load the
transformation module into
Memgraph, then run a
CREATE .. STREAM Cypher query to create a stream.
You need to create one stream for each topic and procedure you have.
Below are basic Cypher queries for starting streams. For more options and
information about the CREATE .. STREAM query and all the other options
regarding streams, such as additional Kafka configuration options, check out the
reference guide.
Kafka and Redpanda
The most basic Cypher query for creating a connection to a Kafka or Redpanda stream is:
CREATE KAFKA STREAM streamName
TOPICS topic1[, <topic2>, ...]
TRANSFORM transModule.transProcedure
BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS bootstrapServers;
Pulsar
The most basic Cypher query for creating a connection to a Pulsar stream is:
CREATE PULSAR STREAM streamName
TOPICS topic1[,topic2, ...]
TRANSFORM transModule.transProcedure
SERVICE_URL serviceURL;
Get information about a stream
You can get the basic stream information with:
SHOW STREAMS;
Check the transformed incoming data
To see the results of the transformation module, use the CHECK STREAM clause.
It will consume the message from the last committed offset but won't commit the
offsets. There is no committed offset coming from a newly created stream, so by
default, Memgraph will wait 30000 milliseconds (30 seconds) for new
messages, and after that, it will throw a timeout exception. You can change the
timeout by adding the TIMEOUT sub-clause and a custom time to the query.
The following Cypher query will transform new messages that come from the stream within 60 seconds:
CHECK STREAM myStream TIMEOUT 60000;
To consume more batches, increase the BATCH_LIMIT:
CHECK STREAM myStream BATCH_LIMIT 3 TIMEOUT 60000;
Start ingesting data from the stream
To start ingesting data, execute the following query:
START STREAM stream_name;
or
START ALL STREAMS;
Your data should be slowly arriving in your Memgraph instance.
Stop or delete a connection to a stream
To stop a stream:
STOP STREAM streamName;
To delete a stream:
DROP STREAM streamName;
For more options, check the reference guide.
Change Kafka stream offset
First, stop the stream if it's running, then use the following Cypher query to change Kafka stream offset if necessary and start it again:
CALL mg.kafka_set_stream_offset(streamName, offset)
An offset of -1 denotes the beginning offset available for the given
topic/partition.
An offset of -2 denotes the end of the stream in which case only the
next produced message will be consumed.
Logs
Errors and notifications regarding streams are contained in Memgraph's log files
which can be found at /var/log/memgraph/memgraph_<date>.log. Look for the name
of your stream in the log file to find the error. You can use the grep command
to search for the stream in the log file:
grep '<stream_name>' /var/log/memgraph/memgraph_<date>.log
What's next?
Take a look at the tutorial we made to help you connect Memgraph and Kafka. Learn more about the query power of Cypher language, or check out MAGE - an open-source repository that contains graph algorithms and modules that can help you tackle the most interesting and challenging graph analytics problems.
You might also be interested in the Graph Style Script language that will help you bedazzle your graphs in Memgraph Lab. Above all, enjoy your graph database!
